How Video Games for Digital Therapy Help Overcome Cognitive and Physical Challenges
Can modern video games serve purposes beyond entertainment — becoming powerful tools for recovery after injuries or improving attention? The latest advances in therapeutic video games show that interactive technologies can radically broaden the potential for brain and body rehabilitation. In this article, we will explore how such games are designed, how they differ from traditional entertainment, and what real-world results researchers and physicians are observing.
What Is Video Game-Based Digital Therapy
The term digital therapy refers to a specific type of medical intervention in which software functions as a treatment or rehabilitation tool. While ordinary games are designed to provide enjoyment, therapeutic games create carefully calibrated challenges that stimulate specific areas of the brain. Their main goal is to trigger neuroplasticity — the brain’s natural ability to change and reorganize under external stimuli.
Neuroplasticity allows nerve cells to reconfigure, form new connections, and restore lost functions after illness or injury. In clinical practice, this mechanism is considered key to effective neurorehabilitation. It is important to note that therapeutic games are developed not only by programmers but also by professional neuroscientists to ensure that the user’s individual needs are taken into account.
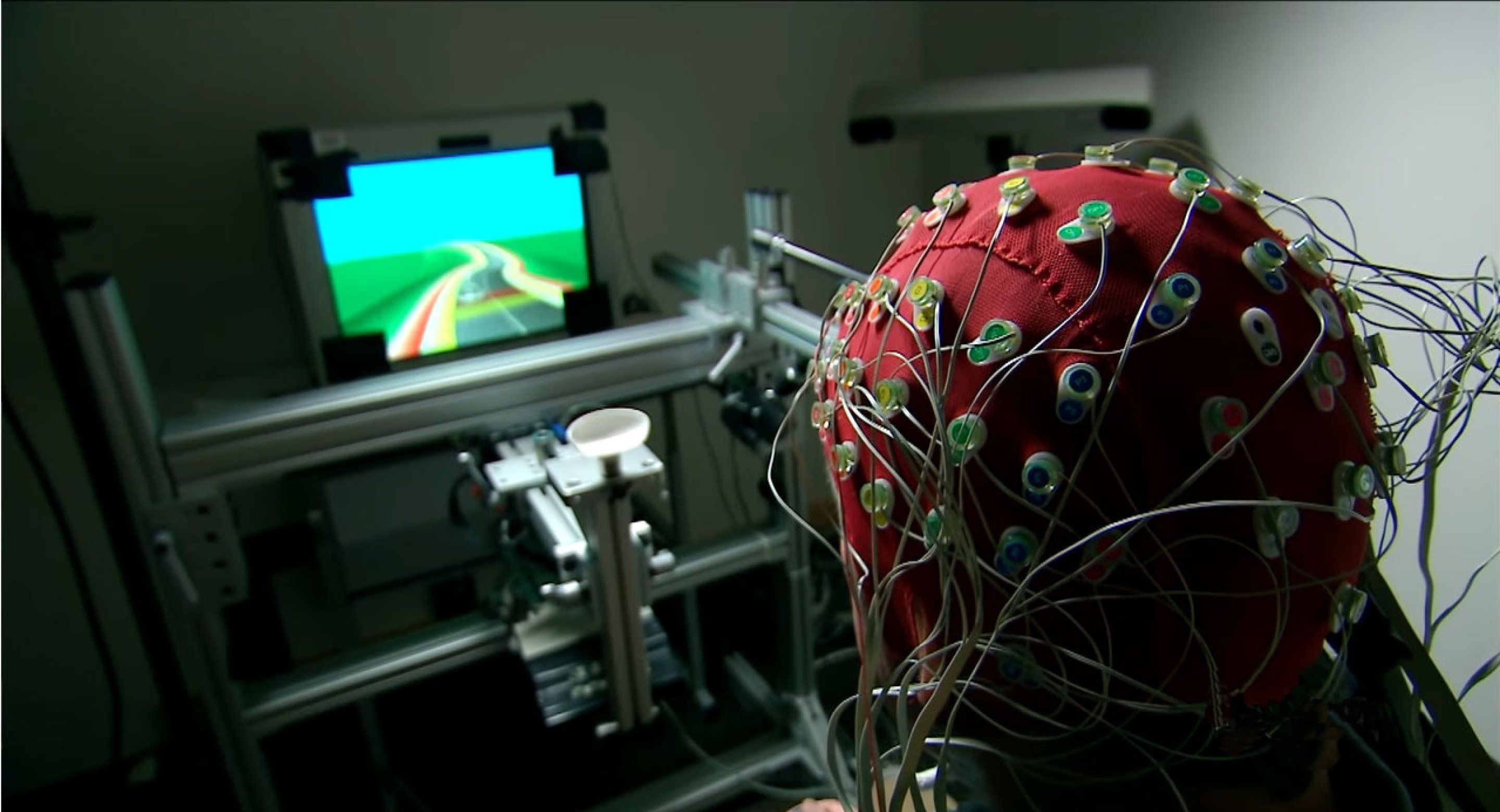
How Therapeutic Video Games Work
Most effective therapeutic video games are built on the principle of a “closed loop”. This means that the gameplay continuously adapts to the user’s current abilities, maintaining an optimal balance between comfort and challenge. The player does not face the usual win-or-lose scenario — instead, the software monitors reactions, adjusts the level of difficulty, and precisely regulates the load on specific cognitive or motor processes.
Tony Simon, a leading cognitive science expert at Northwestern University, notes: “The brain is an organ that depends on activity and external stimulation. In digital therapy, you can’t just ‘swallow’ the desired behavior like a pill — it must be formed.” According to Simon, the key task is to keep the patient in a state of maximum engagement, since that is when the neurocognitive effect is achieved.
Real Examples and Results of Therapeutic Games
Laboratories and medical institutions already showcase vivid examples of successful digital therapies. One of the most notable developments is FastBrain, designed for children with the rare genetic disorder 22q11.2 syndrome. This condition often leads to reduced intellectual functioning and difficulties in everyday learning. FastBrain focuses on stimulating basic cognitive systems, and according to researchers, after a course of gaming sessions, children show improvements in both behavior and information processing.
Another direction is post-stroke rehabilitation. Here, CogniviveVR, based on virtual reality technology, is used. The patient wears a special headset and performs tasks that adjust to their motor abilities. With regular training — five to six times a week for eight weeks — patients demonstrate noticeable improvements in movement smoothness and coordination. The reliability of these results is confirmed by clinical studies and physicians’ assessments.
For adults and children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), the Endeavor therapy has been created. Unlike conventional medication, it does not simply provide temporary focus but helps form new, lasting neural connections. The gameplay involves completing tasks while simultaneously suppressing distracting stimuli. According to the developers at Akili Interactive and participants in clinical trials, after a course of use, users show significantly improved concentration and overall quality of life.
At the same time, it is important to understand that not all games used in therapeutic contexts need to be strictly medical. Some projects help maintain emotional balance and restore a sense of control through safe experiences of risk. For example, the dynamic game Aviatrix allows users to experience excitement and relieve inner tension by combining elements of instant reaction and visual stimulation. More information about this game can be found at https://www.aviatrix.com.in/. Thanks to short gaming sessions and simple rules, it helps maintain a balance between boredom and engagement — an essential component for sustaining cognitive activity.
Advantages and Differences from Traditional Rehabilitation Methods
Compared with medication-based and classical rehabilitation, digital therapy offers several unique advantages. First, a video game functions as targeted or even personalized medicine: it selects tasks precisely according to the abilities of a specific patient — something impossible with standard drug treatment. Second, the changes brought about by such games are long-lasting because they influence the very structure of neural connections.
Patients report greater engagement and interest in the process, while physicians increasingly observe improvements that persist even months after completing the therapy course. According to some clinical observations, the proportion of patients showing stable progress exceeds 40%.
The Future of Digital Therapies and the Role of XR Technologies
Today, the field is developing rapidly. Leading experts — such as Britain Heller from Stanford University and participants from major development companies — are actively introducing new digital approaches using artificial intelligence and extended reality (XR). XR technologies combine elements of the physical and digital environment, allowing users to immerse themselves in highly realistic, immersive scenarios.
At symposia and scientific meetings such as the Games and XR Symposium, experts discuss ways to integrate gaming solutions into medical practice. New educational programs in game science are emerging, ensuring a steady flow of qualified professionals and innovative ideas.